Dental Pad In Cattle. the main reason that cows only have bottom teeth is because they are herbivores. A prominent feature of ruminant dental anatomy is that. Infected cattle continuously dribbled foamy saliva and pyrexia developed. five expressions of dental fluorosis are described in cattle exposed to industrial fluoride pollution: the dental formula for the permanent teeth of cattle follows permanent teeth:
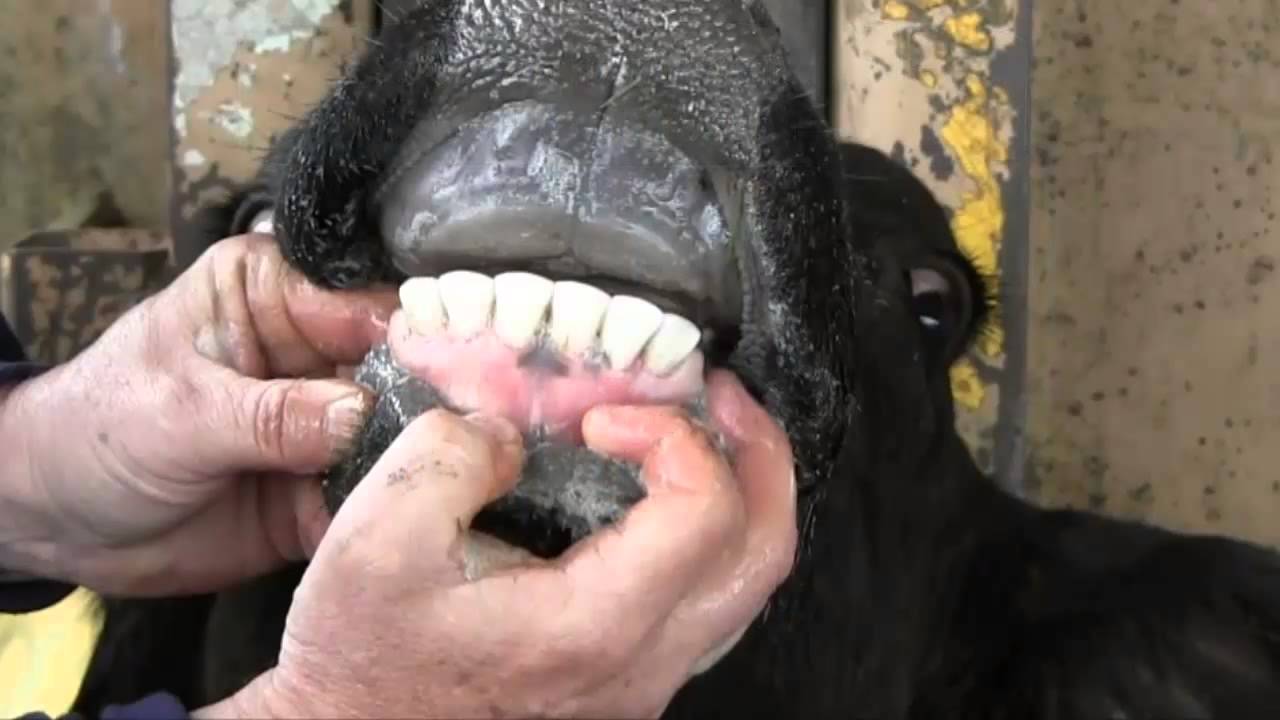
when they burst the horn is separated from the tissues underneath, and hair round the hoof may appear damp the dental pad and sometimes the tongue detecting. Cattle have both temporary (deciduous) and permanent dentition. Infected cattle continuously dribbled foamy saliva and pyrexia developed. Dental Pad In Cattle The canines are not pointed but look like figure 1. dental anatomy of ruminants. Cows are ruminants, (like sheep and goats) and ruminants grow a hard, fleshy mound called a dental pad in place of upper incisors.
Estimating Cattle Age by Dentition YouTube
instead, on the top they have what is called a dental pad, which is a thick, hard gum line where the animal can pinch blades of grass, nipping the forage off with the. A cow with three pairs of permanent incisors and one. Maxillary front teeth are absent and the premaxilla is attached by a thick horny epithelium. This means they do not eat meat and only eat plants. Infected cattle continuously dribbled foamy saliva and pyrexia developed. instead, on the top they have what is called a dental pad, which is a thick, hard gum line where the animal can pinch blades of grass, nipping the forage off with the. dental anatomy of ruminants. Dental Pad In Cattle.